|
Yakovlev Yak-2 (BB-22)1940 |  |
| BOMBER, RECON | Virtual Aircraft Museum / USSR / Russia / Yakovlev |
 |
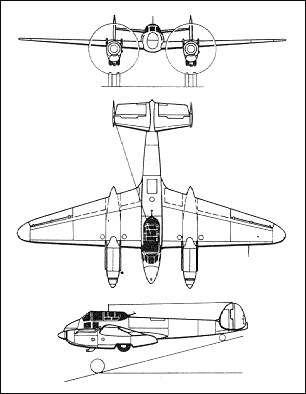
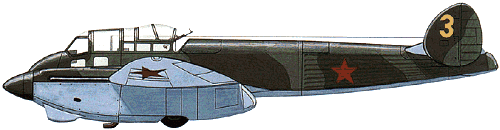
Intended originally as a high-speed reconnaissance aircraft, the Yakovlev Ya-22 prototype was powered by two M-103 engines and made its maiden flight on 22 February 1939. A two-seat low-wing monoplane with wooden wings and a fuselage of mixed construction, the Ya-22 had retractable tailwheel landing gear and a tail unit incorporating a twin fin-and-rudder assembly. Yakovlev was then instructed to modify the design to serve as a bomber, the aircraft being redesignated BB-22 (blizhnii bombardirovshchik or short-range bomber). This resulted in major revisions of accommodation, armament and fuel storage, plus the provision of an internal bomb bay. The first series BB-22 was completed on 31 December 1939 and flown on skis on 20 February 1940 . By that time two factories were in production and experimental variants - the R-12 photographic reconnaissance aircraft and I-29 (or BB-22IS) long-range escort fighter - were being prepared for test flights. The BB-22 was redesignated Yak-2 at the end of 1940, and as powered by two 716kW M-103 Vee engines had a maximum speed of 530km/h at sea level service ceiling of 8800m and range of 800km. In 1940 the basic design was further refined to improve the crew positions, field of view and armour protection; the M-105 engine was introduced with better protection for the fuel system, and provisions were made for external bomb racks. Then redesignated Yak-4, the aircraft entered production in the autumn of 1940 and about 600 of both versions were built, the majority of them Yak-4s . They were not particularly successful in service, many of them being lost in the early days of the German invasion. Yakovlev Yak-2 (BB-22) on YOUTUBE
|  COMPANY PROFILE | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |

|