|
| One of the
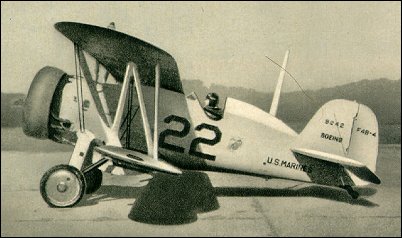
most famous of Boeing's biplane fighters of the inter-war years, the F4B originated as a private venture to develop a replacement for the US Navy's F2B/F3B carrier-based fighters, which had first entered service in 1928. Although they had only been in service for a very short period, Boeing believed it was possible to refine the design to give improved performance without additional power.
Two very similar prototypes were built: Boeing Models 83 and 89. The former had a spreader-bar axle landing gear and an arrester hook; the latter a split-axle landing gear so that a bomb could be carried beneath the fuselage. In other respects they were virtually identical. Following Navy evaluation in the summer of 1928, 27 were ordered as F4B-1, these combining the split-axle landing gear, bomb carrying provisions and arrester hook. Forty-six F4B-2, delivered in early 1931, had the spreader-bar axle, a tailwheel, Frise ailerons and a neat ring cowling for the engine. They were followed by 21 F4B-3 with a semi-monocoque metal fuselage and 92 F4B-4 which differed by having a larger fin and rudder.
The USAAC ordered ten aircraft similar to the F4B-1 in late 1928, accepting the naval evaluation as being correct. Designated P-12, these differed only by having the arrester hook and other specifically naval equipment deleted. P-12B, of which 90 were built with 317kW Wasp engines, differed very slightly and were followed by 96 P-12C, which were similar to the Navy's F4B-2. P-12D, of which 35 were built, had a more powerful 391kW Wasp engine. Most extensively built of the Army versions was the P-12E. This had a monocoque fuselage, pilot's headrest faired by a turtleback and the more powerful engine of the P-12D. A total of 135 were ordered in 1931, many remaining in service until replaced by P-26A in 1935. The last few of the order were given 447kW Pratt & Whitney R-1340-19 engines and the designation P-12F.
Total production for the Army and Navy amounted to 586 aircraft representing a production record for a basic military design which remained unequalled until the attainment of long production runs during World War II.
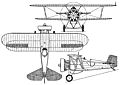 | A three-view drawing of F4B-2 (1653 x 1173) |
| CREW | 1 |
| ENGINE | 1 x P+W R-1340-16, 370kW |
| WEIGHTS |
| Take-off weight | 1551 kg | 3419 lb |
| Empty weight | 1017 kg | 2242 lb |
| DIMENSIONS |
| Wingspan | 9.1 m | 30 ft 10 in |
| Length | 6.2 m | 20 ft 4 in |
| Height | 3.0 m | 10 ft 10 in |
| Wing area | 21.1 m2 | 227.12 sq ft |
| PERFORMANCE |
| Max. speed | 301 km/h | 187 mph |
| Cruise speed | 257 km/h | 160 mph |
| Ceiling | 8380 m | 27500 ft |
| Range w/max.fuel | 1335 km | 830 miles |
| Range w/max payload | 645 km | 401 miles |
| ARMAMENT | 2 machine-guns, 210kg of bombs |
| Frank Donovan, e-mail, 24.01.2024 06:23 I am so happy to have consulted RAPID RESCORE CREDIT for my credit repairs. I discovered that I had 5 negative items on my credit most especially IRS, delayed payments and loans and over 7 hard inquiries from every bureaus and it hindered me from moving forward in my business. I could not access any loan so I started looking for ways to salvage my condition, I then discovered this specialist (RAPID RESCORE CREDIT) on reddit though there were other ones there but my instinct directed me towards Mr Jackson. I was asked for funds to get started with the job and I gave them the benefit of doubt and made some commitments. My fico score was moved from 609 to an excellent score (799) and all the negatives were deleted from my report. Right now I have a clean profile with wonderful trade lines. I’m recommending their services to anyone in dire need of credit fix, you can reach them via JACKSONRAPIDCREDITSCORE@GMAIL.COM reply | | Morgan Kennedy, e-mail, 10.12.2023 08:28 Mr. Jerry and I have worked together for many years now in a professional setting. I am a realtor and have clients in various stages of credit repair. Mr. Jerry is ALWAYS the person I recommend to my clients. His services are second to none & he has always done the best job in order to get my clients in a home as quick as possible when credit is holding them back. He has helped my family members, friends, & strangers I have met through my services. Thank you Mr. Jerry for caring about people like you do! You are making a difference!!! Reach out to Jerrylink Credit Group via: jerrylinkgroup@gmail.com or text 6265140620. Thank me later. reply | | Arkonbey, e-mail, 02.04.2011 04:51 @John: according to the instructions of the Hasegawa 1 /32 kit, the bulge is a fuel tank. reply | | john, e-mail, 09.11.2010 03:14 What is the large bulge under the fuselage? reply | |
| | Bob Tufo, e-mail, 02.08.2010 06:32 I always admired the f4b2, and /or the P-12, and since I flew a Stearman with the P&W1340 can imagine myself at the controls; sweet dreams. reply | | Jim Rhoades, e-mail, 05.09.2010 02:36 My father (W.E "Dusty" Rhoades) flew these in Hawaii with the Army Air Corps during the 1930's. The aircraft had a nasty habit of losing it's tailplane during high speed dives & pullouts. This happened to dad during a practice dogfight resulting in him bailing out at low altitude over a cane field. reply | | Jay, e-mail, 21.08.2008 00:01 I wanted to know the registration number of any F4B that took its first flight on or around 05Nov1929, or was completed on 05Nov1929
Thank you reply | | Frank Hannegan, e-mail, 25.05.2008 01:36 Very informative. My father earned his Navy Wings in '31 and flew the F-4B-4 from the USS LEXINGTON for two years. He said it was a very good aircraft, but when he flew the New Grumman F-3F in the late 30s the new aircraft stole his allegiance. reply |
|
Do you have any comments?
|
| 
COMPANY
PROFILE
All the World's Rotorcraft
|